Alteryx Engine and AMP: Main Differences
In the Alteryx AMP Engine article, we cover the Alteryx Engine and the new Alteryx Multi-threaded Processing (AMP). Here, we go deeper into the main differences between the two.
Data Processing Differences
The original Engine architecture allows for mostly single-threaded processing, where your data are processed record-by-record sequentially. On the other hand, the new AMP concept allows for massively multi-threaded processing. Records process in 4 MB packets for a faster run time, and in parallel, which can affect the output record order.
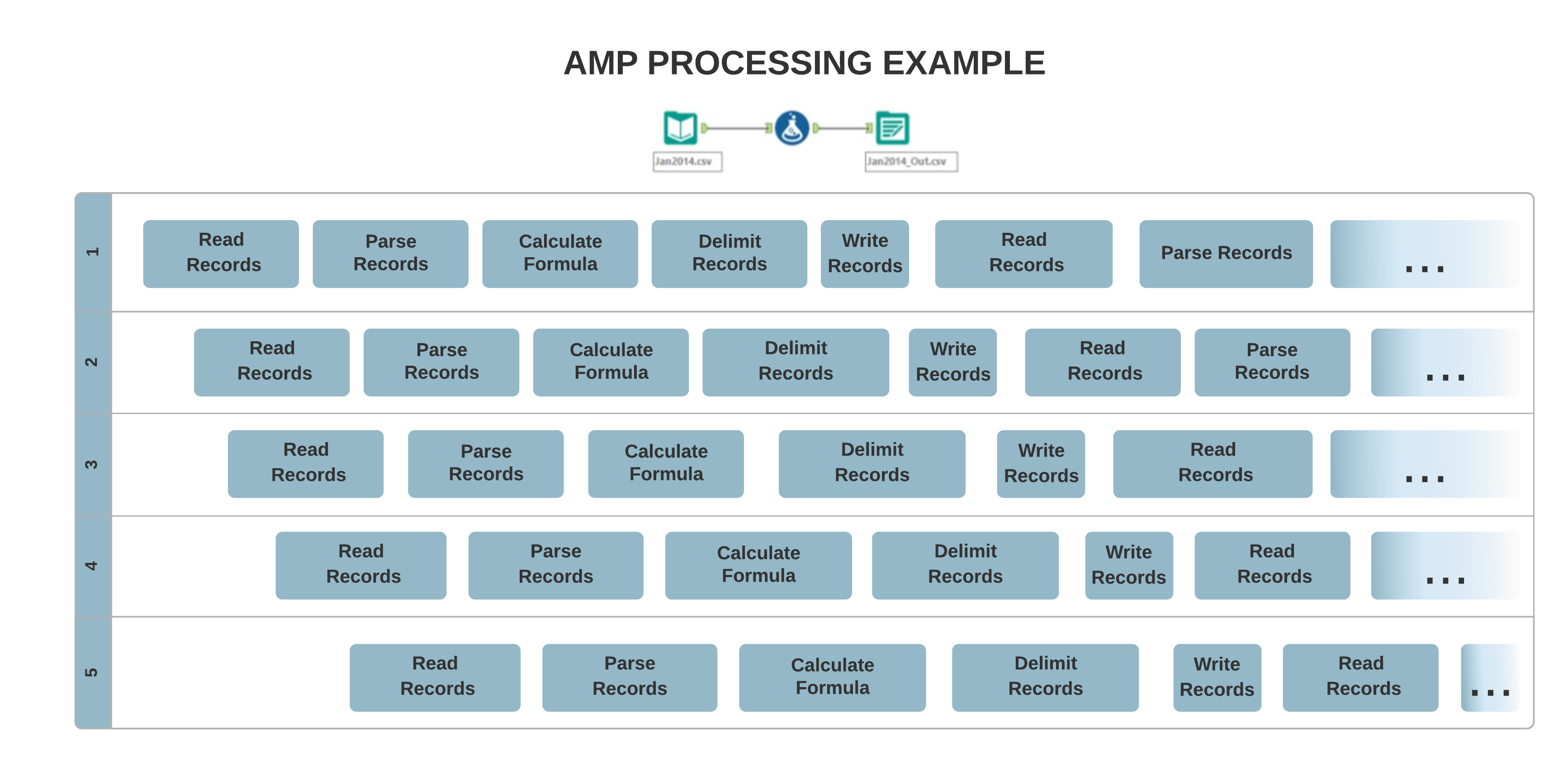
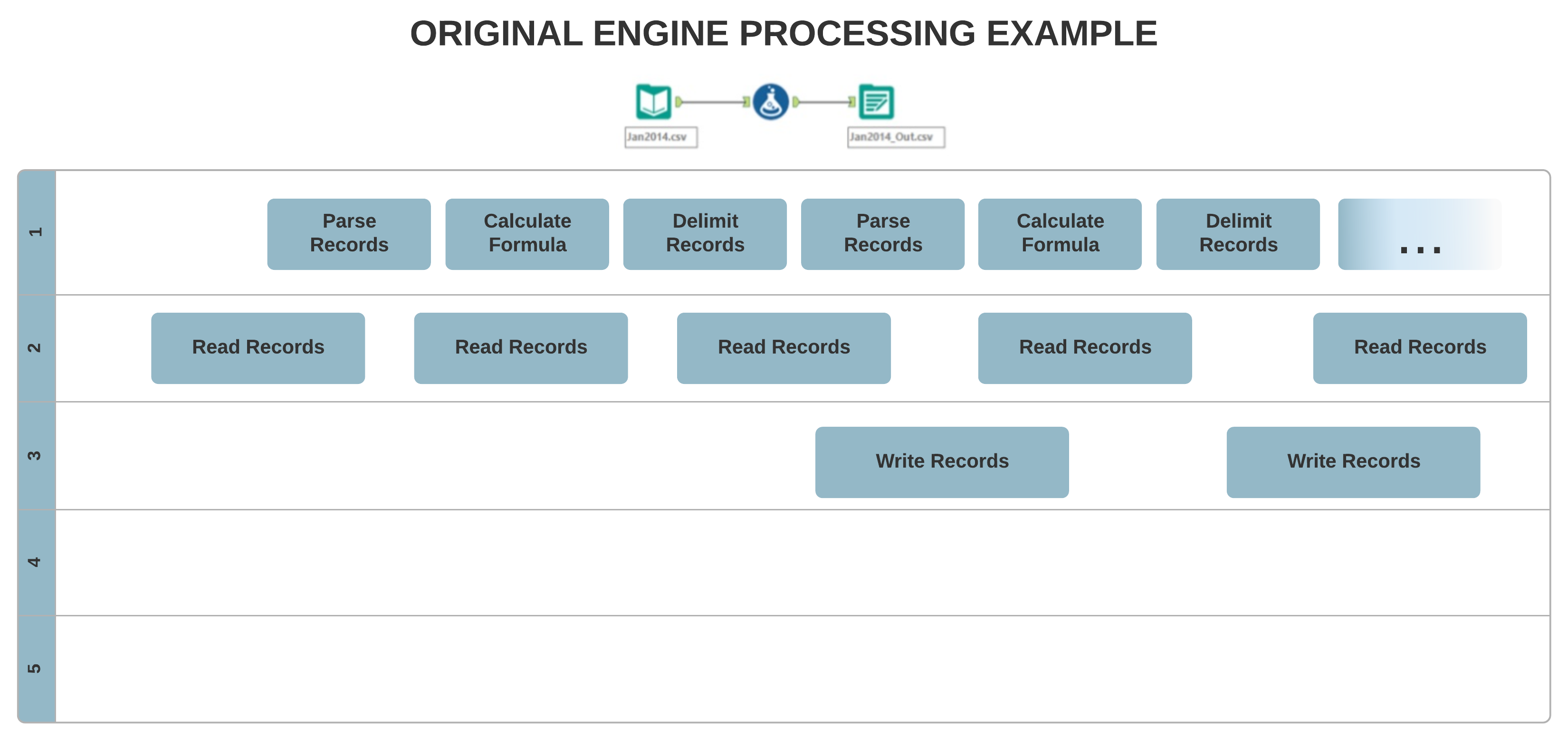
Input Differences
CSV files that contain a field with quoted newlines fail if you don't enable the additional option AMP only: quoted fields can have newlines in them.
Record Limit
The workflow configuration runtime setting Record Limit for all inputs is enabled with AMP for these tools:
Input Data
Text Input
Generate Rows
Macro Input
AMP support for the tool-level Record Limit in the Dynamic Input tool was added with the 2021.1 Patch 2 and all subsequent Releases.
Output Differences
When a workflow runs with the AMP engine, several tools might output records in a different order than the original engine. Some of those tools include...
Cross Tab
Data Cleansing (when removing null rows)
Join
Join Multiple
Multi-Row Formula
Poly Build
Running Total
Sort (when Dictionary Sort is used with special characters)
Summarize (when Group By is used)
Tile
Union
Unique
If your workflow requires records from the above tools to be in a specific order for downstream operations, the Engine Compatibility Mode setting is available to maintain the same sort order as the original Engine. Use this after careful consideration of the specific workflow, mainly when migrating workflows that were created with the original Engine to run with AMP engine.
Specific functionality or configuration that has not been converted to AMP reverts to the original Engine tool in order to work. Therefore workflows that contain both AMP-converted and non-converted tools run seamlessly with AMP.
If you have questions as to which tools have been converted to AMP, go to Tool Use with AMP.
With the original Engine tools are more connected and stop working as soon as there is nothing downstream. With AMP parallel running, the tools might not stop with the empty downstream. The assumption is that with the empty downstream, the data stream is not taken into account. The log message is just for information. If the number of records in the stream is important to you, you can put a Test tool on it and have it produce an error message if it doesn't get the right number of records.
Read Performance
A YXDB file written with the AMP engine reads in faster than a YXDB written with the original Engine. The YXDB file written with the original Engine reads slower with AMP enabled. However, the formats are still compatible.
Use XLSX, CSV, YXDB, and SQLite file formats with AMP—they support multi-threaded, read-in data.
Converting records and packaging between the original Engine and AMP when reading Zip files has a performance cost. This might cause larger Zip files to read significantly slower with AMP.
Tip
When opened in a text editor, a YXDB file written with AMP has "Alteryx e2 Database file" at the very beginning of the file content. A file written with the original Engine has "Alteryx Database File" at the same location.
Write Performance
To improve the original Engine performance (make AMP write a YXDB file created with the original Engine), go to the Output Data - Configuration menu, where you have the option to create a version of the YXDB file compatible with Designer 18.1 and older.
The Output tool behaves differently with records that contain SpatialObj data when you save a CSV file with the original and AMP engines. While AMP writes SpatialObj data into the file when it saves as a CSV file, the original Engine doesn’t. This difference causes file size differences and you might experience decreased performance.
If needed, a workaround is to remove the spatial data from the records via the Select tool. This allows both engines to complete with a similar duration.
Performance Profiling
Performance Profiling per tool with AMP is available with Designer versions 2021.3 and newer.
R Tool Performance
AMP passes data to and from R in the original Engine format. This double conversion takes time. Single R tool execution time can be slower with AMP than with the original Engine, but is faster if more than one branch is run simultaneously.
Text Input Tool and AutoField
AMP addresses a historic issue where the size of the field might not be large enough when processed by a downstream tool. You don't need to add Select tools to change data types when the resulting data exceeds the length of the original data type. AMP creates the maximum size field for strings and integers so that subsequent operations have the necessary room to hold larger downstream values.
Throttle Tool
Although the Throttle tool was not fully converted to AMP, you can use it together with the Download tool (Throttle first).
Fuzzy Match
Fuzzy Match might have different results between the original Engine and AMP. AMP records are matched using an alternative method. The order of match might be different and the output might be in reverse order as well. There is a known performance issue where Fuzzy Match is less performant with AMP than the original Engine.
RegEx Tool
AMP uses Unicode and Perl encoding standards, where the characters $, +, <, =, >, ^, |, and ~ don't qualify as punctuation. When you use the formula function REGEX_Replace or the RegEx tool to filter punctuation with the RegEx set [[:punct:]], with AMP you need to change the expression.
Example
REGEX_REPLACE([_CurrentField_],'[[:punct:]]|[\$\+<=>\^`\|~]','')
Grouping Tools and Blocking Tools
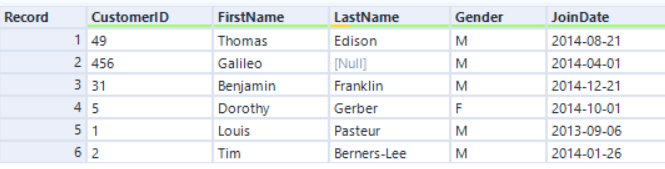
The Join algorithm with the original Engine is based on a sort-merge join method, where the records always come in a sorted order. The new Join algorithm with AMP is based on a hash join method, so the record order comes out disordered. For example...

Left input:
Right input:
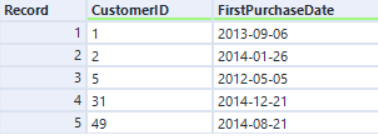
If we join by CustomerID with the original Engine, the record order is sorted by the CustomerID field:
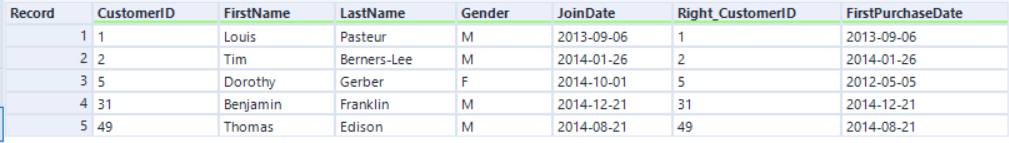
With AMP, records are the same but in a different order:
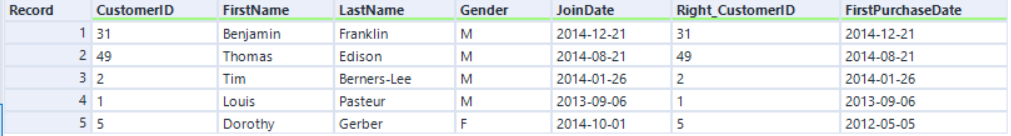
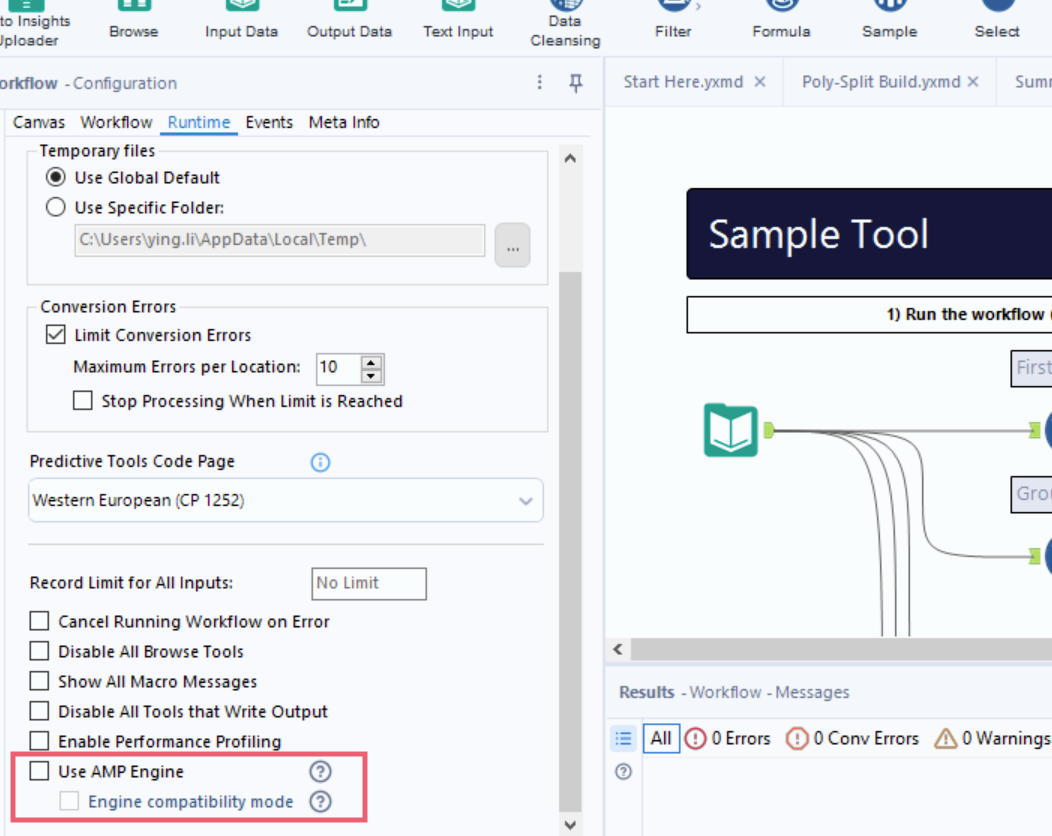
If you need to have sorted order in join output, add the Sort tool after Join or enable the Engine Compatibility Mode setting in Workflow Configuration > Runtime, below the Use AMP Engine setting.
Iterative Macros
The difference between the original Engine and AMP can occur when a tool inside the macro reports an error. Being single-threaded, the original Engine stops if an error occurs in the macro. AMP works until the iterative output is empty or the maximum number of iterations occurs. You can encounter these situations, due to a higher number of iterations:
The number of errors (if any) can be higher with AMP.
The number of records can be higher with AMP.
The output schema can be different with AMP.
Formula Tool
ConvertFromCodePage and ConvertToCodePage functions in the Formula tool accept string as a parameter and return string as a result, so it is not possible to distinguish how the string is encoded. There is a difference in the output of the Formula tool with these functions used with the original Engine and AMP.
A different binary representation of the input data is caused by AMP's internal use of UTF-8 encoded strings. When the data with a different encoding is imported, there is no way to restore the original data. The original Engine stores strings as Latin-1 or UTF-16 encoded strings that were used as a buffer and allows to convert data back correctly.
Formula Add-Ins
Formula Add-Ins are not yet supported with AMP. If you need to run a workflow that contains Formula Add-In functionality, run it on the original Engine.
Analytic App
Apps that use the Map tool to select from a spatial reference layer in an Analytic App should continue using original Engine.
Expect Equal
With the original Engine, Expect Equal remains a CReW macro. With AMP it runs as a native tool.
Parallel Branch Execution and Tool Run Order
Some workflows read from a file and then write back to it. This requires sequencing to ensure that the read is complete before the write can start. Similarly, a workflow that wants to write several sheets in one XLSX file needs to write the sheets one at a time. Alteryx Designer provides a Block Until Done (BUD) tool to help partition the work into phases that won’t get in each other’s way.
Same workaround is applicable for Email tool when you use output file(s) from previous branch(es) as attachment. You need to wait once data processing is complete and then add as attachment to the Email tool.
When you work on a workflow with multiple branches (largely separate streams from inputs to outputs), place the BUD tool in the workflow branch with the lowest numbered Input tool ID. This ensures every subsequent branch waits to run until the previous branch is done and the tool works as expected.
Available Functionality
For more information regarding specific tool functionality, go to Tool Use with AMP.