COSH Function
Computes the hyperbolic cosine of an input value for a hyperbolic angle measured in radians. The value can be a Decimal or Integer literal or a reference to a column containing numeric values.
A hyperbola is the shape created by taking a planar slice of two cones whose tips are touching each other. For two identical cones, the curves of the slices mirror each other, no matter the angle of the plane through the cones.
The two slices represent the set of points on a grid such that:
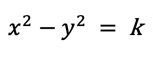
where
kis some constant.The hyperbolic trigonometric functions measure trigonometric calculations for the right-side (x > 0) slice of the hyperbola.
For more information, see https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hyperbola.
The hyperbolic cosine (COSH) function is computed using the following formula:
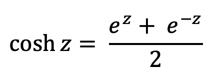 |
Hyperbolic secant:
The hyperbolic secant is the following:
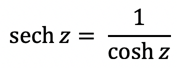 |
You can convert from degrees to radians. For more information, see RADIANS Function.
Wrangle vs. SQL: This function is part of Wrangle, a proprietary data transformation language. Wrangle is not SQL. For more information, see Wrangle Language.
Basic Usage
Numeric literal example:
round(cosh(radians(30)),3)
Output: Returns the computation of the hyperbolic cosine of a 30-degree angle, which is converted to radians before being passed to the COSH function. The output value is rounded to three decimals: 1.140.
Column reference example:
cosh(X)
Output: Returns the hyperbolic cosine of the radians values in X column.
Syntax and Arguments
cosh(numeric_value)
Argument | Required? | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
numeric_value | Y | string, decimal, or integer | Name of column, Decimal or Integer literal, or function returning those types to apply to the function |
For more information on syntax standards, see Language Documentation Syntax Notes.
numeric_value
Name of the column, Integer or Decimal literal, or function returning that data type to apply to the function.
Missing input values generate missing results.
Literal numeric values should not be quoted. Quoted values are treated as strings.
Multiple columns and wildcards are not supported.
Usage Notes:
Required? | Data Type | Example Value |
|---|---|---|
Yes | String (column reference) or Integer or Decimal literal | 0.5 |
Examples
Tip
For additional examples, see Common Tasks.
Example - Hyperbolic trigonometry functions
This example illustrates how to apply hyperbolic trigonometric functions to your transformations. All of the functions take inputs in radians.
Functions:
Item | Description |
|---|---|
SINH Function | Computes the hyperbolic sine of an input value for a hyperbolic angle measured in radians. The value can be a Decimal or Integer literal or a reference to a column containing numeric values. |
COSH Function | Computes the hyperbolic cosine of an input value for a hyperbolic angle measured in radians. The value can be a Decimal or Integer literal or a reference to a column containing numeric values. |
TANH Function | Computes the hyperbolic tangent of an input value for a hyperbolic angle measured in radians. The value can be a Decimal or Integer literal or a reference to a column containing numeric values. |
The following functions can be computed based on the inverse of the above functions:
Hyperbolic Cotangent. Computed as 1/TANH.
Hyperbolic Secant. Computed as 1/COSH.
Hyperbolic Cosecant. Computed as 1/SINH.
Also:
Item | Description |
|---|---|
ROUND Function | Rounds input value to the nearest integer. Input can be an Integer, a Decimal, a column reference, or an expression. Optional second argument can be used to specify the number of digits to which to round. |
RADIANS Function | Computes the radians of an input value measuring degrees of an angle. The value can be a Decimal or Integer literal or a reference to a column containing numeric values. |
DIVIDE Function | Returns the value of dividing the first argument by the second argument. Equivalent to the |
Source:
In the following sample, input values are in degrees:
X |
|---|
-30 |
0 |
30 |
45 |
60 |
90 |
120 |
135 |
180 |
Transformation:
In this example, all values are rounded to three decimals for clarity.
First, the above values in degrees must be converted to radians.
Transformation Name |
|
|---|---|
Parameter: Formula type | Single row formula |
Parameter: Formula | round(radians(X), 3) |
Parameter: New column name | 'rX' |
Hyperbolic Sine:
Transformation Name |
|
|---|---|
Parameter: Formula type | Single row formula |
Parameter: Formula | round(sinh(rX), 3) |
Parameter: New column name | 'SINHrX' |
Hyperbolic Cosine:
Transformation Name |
|
|---|---|
Parameter: Formula type | Single row formula |
Parameter: Formula | round(cosh(rX), 3) |
Parameter: New column name | 'COSHrX' |
Hyperbolic Tangent:
Transformation Name |
|
|---|---|
Parameter: Formula type | Single row formula |
Parameter: Formula | round(tanh(rX), 3) |
Parameter: New column name | 'TANHrX' |
Hyperbolic Cotangent:
Transformation Name |
|
|---|---|
Parameter: Formula type | Single row formula |
Parameter: Formula | round(divide(1, tanh(rX)), 3) |
Parameter: New column name | 'COTHrX' |
Hyperbolic Secant:
Transformation Name |
|
|---|---|
Parameter: Formula type | Single row formula |
Parameter: Formula | round(divide(1, cosh(rX)), 3) |
Parameter: New column name | 'SECHrX' |
Hyperbolic Cosecant:
Transformation Name |
|
|---|---|
Parameter: Formula type | Single row formula |
Parameter: Formula | round(divide(1, sinh(rX)), 3) |
Parameter: New column name | 'CSCHrX' |
Results:
X | rX | TANHrX | COTHrX | COSHrX | SECHrX | SINHrX | CSCHrX |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
-30 | -0.524 | -0.481 | -2.079 | 1.14 | 0.877 | -0.548 | -1.825 |
0 | 0 | 0 | null | 1 | 1 | 0 | null |
30 | 0.524 | 0.481 | 2.079 | 1.14 | 0.877 | 0.548 | 1.825 |
45 | 0.785 | 0.656 | 1.524 | 1.324 | 0.755 | 0.868 | 1.152 |
60 | 1.047 | 0.781 | 1.28 | 1.6 | 0.625 | 1.249 | 0.801 |
90 | 1.571 | 0.917 | 1.091 | 2.51 | 0.398 | 2.302 | 0.434 |
120 | 2.094 | 0.97 | 1.031 | 4.12 | 0.243 | 3.997 | 0.25 |
135 | 2.356 | 0.982 | 1.018 | 5.322 | 0.188 | 5.227 | 0.191 |
180 | 3.142 | 0.996 | 1.004 | 11.597 | 0.086 | 11.553 | 0.087 |