Connection Basics
In Alteryx One Platform, you can quickly connect to default datastores and import your file- or table-based datasets for use in the Alteryx One apps available to you. As needed, you can create connections to other datastores to which you have access and import from them.
Basic Import Process
There are multiple ways to import data into Alteryx One, but the most direct way is to import through the Library, where all imported datasets are stored. In Alteryx One, select the Library icon in the left navigation bar.
Import Data
The Library for Data displays all of the datasets to which you have access. To begin, select Import Data.
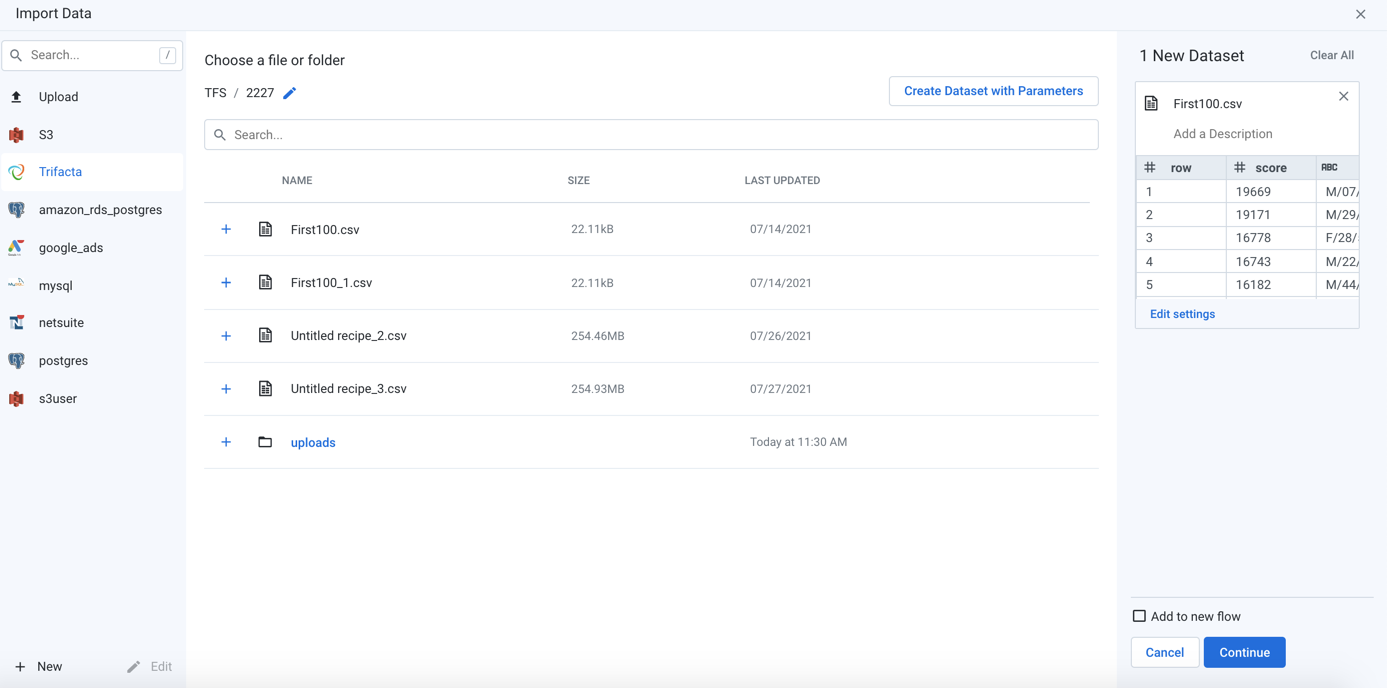
Figure: Import Data Page
When you import data, you are selecting a connection to use, which allows you to begin navigating the connected datastore. When you locate the file or table assets, you select it for import.
Note
When you import a dataset, you are creating a reference to that source dataset. Data is not actually imported until Alteryx One needs to use the data for job execution. Source data is never modified.
Default Connections
Alteryx One provides preconfigured connections to storage. Depending on your environment, you may be able to immediately access data through the following datastores, which are represented by icons in the Import Data page:
Icon | Connection | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Upload | Upload a file from your local desktop. Astuce You can always upload a file from your local desktop for immediate use in the application. Details are below. | |
| File-based storage | Alteryx One provides a connection to a primary file-based storage system. Also known as the base storage layer, this storage can be used for hosting datasets for import. Uploaded files are stored on the base storage layer, as well as dataset samples. | |
| Table-based storage | Your environment may be provided access to a table-based datastore, such as BigQuery or Redshift. From these datastores, you can select the tables or views to which you have access for import as datasets in Alteryx One. | |
| Other storage | You can create connections to other file- or table-based storage systems. See below for details. |



