One Tool Example
Join has a One Tool Example. Visit Sample Workflows to learn how to access this and many other examples directly in Alteryx Designer.
Use Join to combine 2 inputs based on common fields between the 2 tables. You can also Join 2 data streams based on record position.
Select how to perform the Join. The 2 options are: by record position or by a specific field (column).
Join by Record Position: Select this option when the two tables to be joined have the same field structure, and the data will be joined by its position within the two tables.
Join by Specific Field: Select this option when the two tables have one or more fields in common (like an ID) and the data will be joined together. You can choose to Join based on multiple fields. Each Join should be a separate row in the grid.
Potential Error Messages
The Join tool restricts what field types can be joined together. These warnings or errors might occur:
String fields can only be joined to other string fields.
Numeric fields can only be joined to other numeric fields.
Double fields can only be joined to other double fields.
Joins on Double or Float are not recommended due to rounding error.
Boolean fields can only be joined to other boolean fields.
DateTime field types can only be joined to their exact type.
Spatial fields cannot be joined, use the Spatial Match tool instead.
Blob fields cannot be joined to any other type.
Each Input (Left and Right) has a dropdown list where you can select fields (columns). Select the join field for each input. Alteryx Designer automatically selects a join field from an input if the same field name was already selected from a different input. If you need multiple join fields, you can configure an additional row of join fields.
Select the dropdown to choose an additional join field, per input.
To delete a join field, select a number on the left-hand side and select the Delete button.
Use the table in the Configuration window to modify the incoming data stream. Each row in the table represents a column in your data. The Field column in the table identifies the name of each column in the data and auto-sizes to fit column (field) names without cutting off any text (up to 40 characters).
Before you start updating your fields (columns), you might want to limit your list so that you can perform updates on only a subset of the fields. This is also really helpful if your dataset contains many fields.
To do this, you can use the Search box at the top of the Configuration window. Enter a keyword and the Join tool searches the Field, Rename, and Description columns to return matches. The search is not case-sensitive.
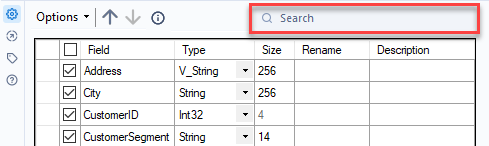
You can then perform various actions (like select, deselect, rename, etc.) on only the fields that were returned via your search. Think of the Search box as a way to filter your list of fields so that you can update only a subset of your data columns.
To view your entire list of fields again, use the "x" icon to clear out the Search box.
Note
After you perform a search, only a subset of your data fields (columns) display. Please note that depending on what action you chose in the Options menu...
Some actions might apply to only fields shown.
Some actions might apply to all fields, regardless of which ones are shown
Some actions might only apply to the specific fields that are selected (highlighted) in the list of fields.
Because of this, please use caution when you perform actions on a subset of fields and double-check the results to make sure they are what you're expecting.
To include a column in the dataset, check the check box to the left of the column name. Uncheck the check box to exclude the column. You can also use the select and deselect all check box at the top of the table to quickly select and deselect all visible fields.
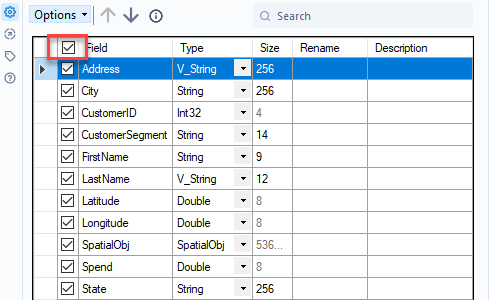
To sort the columns of data based on the column name...
Click on the column name to sort in ascending order.
Click on the column name a second time to sort in descending order.
Sort Method
Depending on the language of your Designer instance, a different default sort order might be used. Consult the Localization User Settings to read more about the default Sort Method.
To reorder the columns of data...
Select to highlight a row, or select and drag to highlight multiple rows.
Use the Move Up or Move Down arrows, or right-click and drag, to move the rows to a new location.
The Unknown column is selected by default. It allows new columns in the data. Move the column to the location where you want a new column to be.
Use the Type dropdown to change the data type of a column in your dataset.
To change the supported length (characters for string, date-time, time, and numeric fixed decimal types) or measurement (bytes for other numeric types) of data in a column, select Size and enter a number. Size varies by data type and you can edit it for fixed decimal numeric types, date-time and time types, and all string types.
Use the [data type]: Forced option to ensure a column always contains the expected data type. This is helpful when creating macros.
To change the name of a column, select the Rename field and enter the new name.
To add a description, select the Description field and enter a description.
After you select or highlight rows (columns of data) in the table, select the Options dropdown above the table to view more configuration options:
Save/Load: Save Field Configuration as a .yxft file. The Alteryx Field Type File is a text file that can be used in other workflows using the Load Field Names or Load Field Names & Types options.
Select: Select or deselect all or highlight columns. Options include Select All and Deselect All.
Change Field Type of Highlighted Fields: Change the data type of all highlighted columns at once.
Sort: Sort the column order in ascending or descending order. Options include Sort on Original Field Name, Sort on New Field Name, and Sort on Field Type, or Revert to Incoming Field Order. Depending on the language of your Designer instance, a different default sort order might be used. Consult the Localization User Settings to read more about the default Sort Method.
Move: Move highlighted columns to the top or bottom of the list.
Add Prefix to Field Names: Add a prefix to the selected or highlighted column name.
Add Suffix to Field Names: Add a suffix to the selected or highlighted column name.
Remove Prefix or Suffix: Remove the prefix or suffix from the selected or highlighted column name.
Clear All Renames: Remove the new name for all columns.
Clear Highlighted Renames: Remove the new name for all highlighted columns.
Revert All to Original Type & Size: Undo all changes to type and size in all columns and use the original values.
Revert Highlighted to Original Type & Size: Undo changes to type and size in the selected or highlighted columns and use the original values.
Forget All Missing Fields: Remove all columns that are no longer included in the data.
Forget Highlighted Missing Fields: Remove all highlighted columns that are no longer included in the data.
Deselect Duplicate Fields: Deselect the second column when duplicate column names exist. This option is only available with multiple inputs.
The 3 outputs that result from the join are...
L anchor | Contains records from the L input that didn't join to records from the R input. | 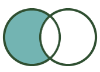 |
J anchor | Contains records that joined from the L input to the records in the R input. | 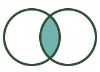 |
R anchor | Contains records from the R input that didn't join to records from the L input. | 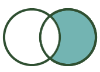 |
Reference this table to use the Join tool to execute different types of joins.
Inner Join: Contains records that joined from the L input to those records in the R input. | 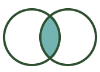 |  | The J output of the Join tool contains the result of an Inner Join. |
Left Unjoin: Contains records from the L input that did NOT join to records from the R input. | 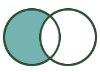 | 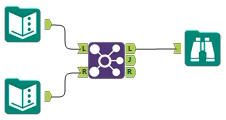 | The L output of the Join tool contains the result of a Left Unjoin. |
Right Unjoin: Contains records from the R input that did NOT join to records from the L input. | 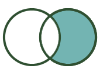 | 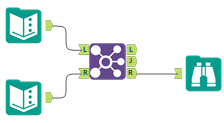 | The R output of the Join tool contains the result of a Right Unjoin. |
Left Outer Join: All records from the L input including the records that joined with the R input. | 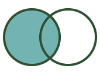 | 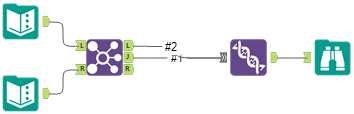 | To do a Left Outer Join, connect the J and L outputs of the Join tool to the Union tool. Connect the J output first to establish the combined table schema. |
Right Outer Join: All records from the R input including the records that joined with the L input. | 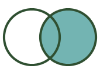 | 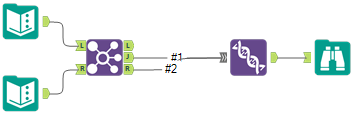 | To do a Right Outer Join, connect the J and R outputs of the Join tool to the Union tool. Connect the J output first to establish the combined table schema. |
Full Outer Join: All of the records from both L and R inputs. | 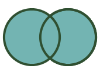 |  | To do a Full Outer Join, connect the J, L, and R outputs of the Join tool to the Union tool. Connect the J output first to establish the combined table schema. |

