Use Download to retrieve data from a URL to use in downstream processing or to save to a file. The Download tool can also download or upload data via FTP and SFTP.
Non-FIPS Designer releases starting with 2022.3 have Peer Validation enabled by default. Go to Peer Validation Allow List to learn how to specify a list of problematic hosts in a flat file for which peer validation should be skipped.
Use the Basic tab to set the mandatory controls for the Download tool.
URL Field: Specify the field from the incoming data stream that contains the URL (Uniform Resource Locator - Internet resource) to pull data from (or upload data to). This could simply be a Text Input tool where the URL is specified as a field value.
When using the Download tool with DCM, the URL that data will be pulled from is split into 2 parts. The base of the URL is fetched from the DCM Data Source definition while the latter part (that is appended to the base URL) is fetched from the incoming data stream.
Encode URL Text: Select to encode the URL so unsafe ASCII characters are converted into a format that can be transmitted over the internet. An example of this is the substitution of %20 for a space.
Output: Specify how the returned data is formatted. The data can be returned in a data field or output to a file.
To a Field: Downloaded content is returned in the data stream as a data field. The downloaded contents are in a single field called "DownloadData." You might have to parse this data using downstream tools like the Text To Columns tool, RegEx tool, or Formula tool.
String: Data is returned as a new, wide, string-type field. A wide string supports Unicode® characters. Select one of the Code Pages to use for encoding. The default is UTF-8. For the most consistent results, applications should use Unicode, like UTF-8 (code page 65001) or UTF-16, instead of a specific code page.
Blob: Data is returned as a new blob-type field. Blob is also known as Binary Large OBject. Image files are usually stored in this format. To use the image, configure an Image tool downstream and specify Image or Blob field.
To a File
Temporary File: Data is output to a temporary file located in the user's temporary directory. For more on temp file handling in Designer, go to Alteryx and Temporary Files.
Filename from a Field: Data is output to a specific file where the file specification is in an incoming field. Use the dropdown to select the field that contains the file name to output to.
Use the Headers tab to modify the HTTP headers sent with the web request.
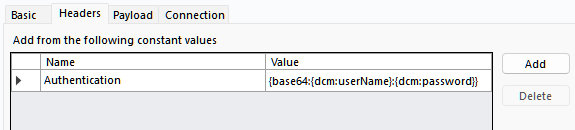
Add from the following constant values: Allows for adding fixed header values.
For example, to add the header "Accept: text/plain"...
Select the Add button.
Enter "Accept" in the Name field and "text/plain" in the Value field.
And values from these fields: Takes values from the record data and creates header values.
For example, to add the header "Expect: 100-continue", select a field from the input data named "Expect" that contains "100-continue."
Use the Payload tab to set the HTTP Action you want to perform and optionally build the Query String or Body for the web request.
HTTP Action: Select the HTTP Action for the web request:
GET (or FTP): Perform a GET request or download a file from an FTP or SFTP site. You don't have to enter any other options on this tab to download the data from your selected URL.
POST: Perform a POST request to the selected URL. Typically when using this option you specify a POST body using the below options.
PUT: Perform a PUT request. This option only allows you to take the query body from a blob field via the Blob Input tool. Typically used to upload a file to the remote server.
DELETE: Perform a DELETE request. Typically used to ask the remote server to delete a specified resource.
HEAD: Perform a HEAD request. This asks the server to return the header data, but not the body data.
Custom: Use this option to enter a custom verb in a text box. Everything else about this request behaves the same as a POST. The POST verb is replaced by the custom verb just before the request is made.
Verb Support
These options only work if the remote server that you send the requests to supports a particular verb. Check the API documentation of the URL you are using to see which requests are supported.
Choose from these Query String/Body options:
Compose Query String/Body:
From the Following Constant Values: Add constant name-value pairs to the query string/body
And values from these fields: Take name-value pairs from the incoming data record. The field name is the name used in the Query String/Body.
Content-Type: Control how the name-value pairs are encoded.
Application/x-www-form-urlencoded: For example, Name1=Value1&Name2=Value2&Name3=Value3. Unsafe ASCII characters are automatically encoded, so make sure your data is not already encoded.
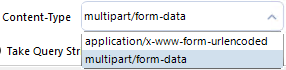
Multipart/form-data: Only available when using the POST and Custom HTTP Actions.
Take Query String/Body from Field: Select the field in the input data that contains the Query String/Body data. You can select Blob fields when you use the POST, PUT, and Custom HTTP Actions.
Use Following for Query String/Body: Manually enter the Query String or Body contents.
All text data is UTF-8 encoded before it's sent to the remote web server.
Use the Connection tab to set up connection credentials.
Username (Optional): Enter the user name if required by the URL specification above. This is an optional field.
Password (Optional): Enter the password if required by the URL specification above. This is an optional field.
The credentials above are used for basic authentication.
Maximum Connections: Specify the maximum number of simultaneous transfers for the Download tool to perform. Transfers are only done in parallel when there are multiple input records sent to the Download tool. Multiple Download tools operate independently but don't typically function at the same time. For new Download tools added to a workflow, the default number of connections is 2 and the maximum number of connections is 32.
Increasing the number of connections might reduce the total time taken to complete all transfers, but use caution not to set the number too high as it could overload the server being used. It is possible the server could quit responding, report errors, or even refuse connections if it believes you are misusing it. This is particularly important when accessing a public site that is not under your control. Most web browsers will do as many as 6 simultaneous transfers, but these would typically be relatively small transfers as a part of a web page. For a server inside your own business where you have more control over how it is configured, using a higher number of connections might be okay.
Additionally, because the Download tool sends records downstream as transfers complete, it might result in a change in the order of records as they pass through the tool. If the order matters, make sure to sort the results or limit the number of connections to 1. Finally, note that empty URLs are processed ahead of those that require an actual transfer.
Timeout (seconds): Specify the number of seconds to wait before reporting a timeout due to an unresponsive connection. Select a number from 0 (never timeout) to 10,000.
Throttle Records: (unchecked by default) Check to limit the number of records that pass through the tool in a given minute. This is useful for specifying the number of requests sent per minute when there are limits to how many records can be processed.
Records Per Minute: Check the Throttle Records checkbox directly above to customize the number of records that you want to pass through the tool per minute.
The default value is 60.
The acceptable range is between 0 and 60,001 (not inclusive).
The Download tool's DCM support facilitates authentication to API endpoints through Basic authentication. It also enables the resolution of values stored in DCM within the request Header or Payload constants when sending PUT and POST requests. This is achieved by allowing the encoding of specific portions of the Header or Payload values using base64 encoding. The encoding works with the DCM expanded values, allowing you to include a credential from DCM and encrypt it with base64.
Select the Use Data Connection Manager (DCM) checkbox to set up the connection using DCM. For more information, go to DCM - Designer.
Resolve DCM Credentials on Payload in PUT and POST Requests
Select the Resolve on Payload checkbox to use DCM-specific aliases for Headers and Payload settings. YOu can use The aliases for both Name and Value while only the Compose Query String/Body option is supported for Payload. Once you run the workflow, these aliases are automatically replaced by the corresponding DCM values.
These are the supported aliases:
{dcm:userName}
{dcm:password}
{dcm:host}
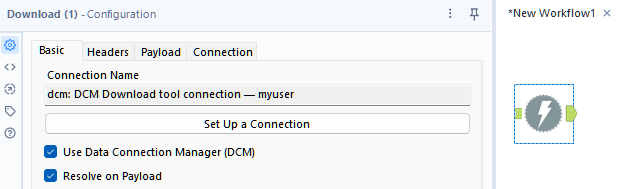
Add the Download tool to the canvas, select a DCM connection, and make sure the Resolve on Payload checkbox is checked.
On the Headers or Payload tabs, based on your target endpoint requirement, you can add a constant and use either
{dcm:userName}or{dcm:password}inside the Value column. You can combine multiple DCM references or include a custom string. For example, you can create a header Authentication with the value of{dcm:userName}:{dcm:password}.If you're looking to resolve DCM secrets as part of the Payload body within a POST request, make sure to select the multipart/form-data option from the Content-Type dropdown, as Alteryx doesn't allow secret expansion of secrets within URL for security reasons.
Base64 Encoding
On the Download tool configuration pane, you can use the {base64:yourtextgoeshere} tag to wrap any string in Header or Payload constant values. You can combine this with any other string or even the DCM tags described above if you want to base64 encode the DCM referenced values.
You can use the following as the Authentication header value {base64:{dcm:userName}:{dcm:password}}, encoding the combination of the username and password as stored in DCM.
To avoid connection delays when you use the Download tool, ensure that the "Automatically detect settings" option is deselected within your account’s internet properties (Control Panel > Internet Options > Connections > LAN Settings).

